The documentation you are viewing is for Dapr v1.9 which is an older version of Dapr. For up-to-date documentation, see the latest version.
Quickstart: Service-to-component resiliency
Note
Resiliency is currently a preview feature.Observe Dapr resiliency capabilities by simulating a system failure. In this Quickstart, you will:
- Execute a microservice application with resiliency enabled that continuously persists and retrieves state via Dapr’s state management API.
- Trigger resiliency policies by simulating a system failure.
- Resolve the failure and the microservice application will resume.
Select your preferred language-specific Dapr SDK before proceeding with the Quickstart.
Pre-requisites
For this example, you will need:
Step 1: Set up the environment
Clone the sample provided in the Quickstarts repo.
git clone https://github.com/dapr/quickstarts.git
In a terminal window, navigate to the order-processor directory.
cd ../state_management/python/sdk/order-processor
Install dependencies
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
Step 2: Run the application with resiliency enabled
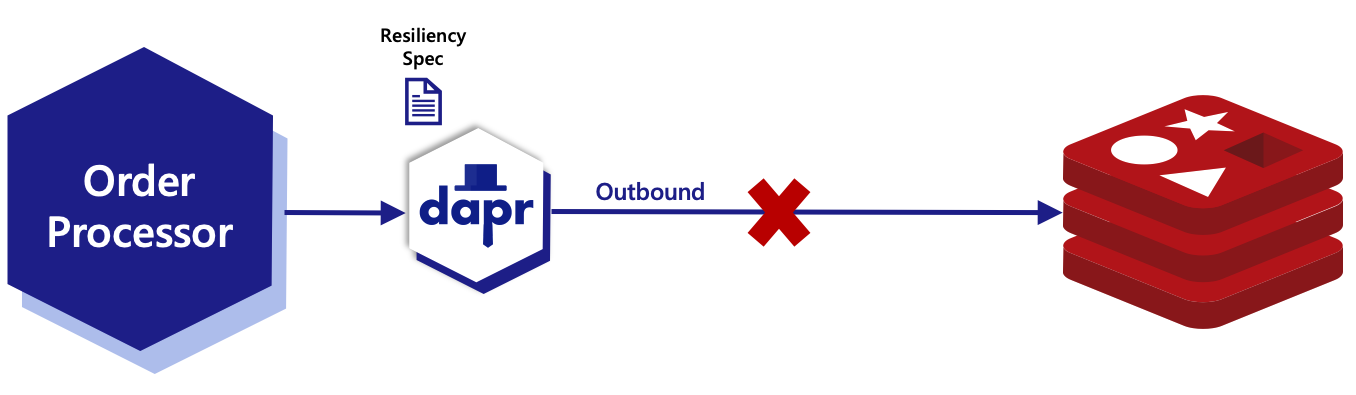
Run the order-processor service alongside a Dapr sidecar. In the dapr run command below, the --config parameter applies a Dapr configuration that enables the resiliency feature. By enabling resiliency, the resiliency spec located in the components directory is loaded by the order-processor sidecar. The resilency spec is:
apiVersion: dapr.io/v1alpha1
kind: Resiliency
metadata:
name: myresiliency
scopes:
- checkout
spec:
policies:
retries:
retryForever:
policy: constant
maxInterval: 5s
maxRetries: -1
circuitBreakers:
simpleCB:
maxRequests: 1
timeout: 5s
trip: consecutiveFailures >= 5
targets:
apps:
order-processor:
retry: retryForever
circuitBreaker: simpleCB
dapr run --app-id order-processor --config ../config.yaml --components-path ../../../components/ -- python3
Once the application has started, the order-processorservice writes and reads orderId key/value pairs to the statestore Redis instance defined in the statestore.yaml component.
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '1' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '1' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '2' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '2' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '3' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '3' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '4' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '4' }
Step 3: Introduce a fault
Simulate a fault by stopping the Redis container instance that was initialized when executing dapr init on your development machine. Once the instance is stopped, write and read operations from the order-processor service begin to fail.
Since the resiliency.yaml spec defines statestore as a component target, all failed requests will apply retry and circuit breaker policies:
targets:
components:
statestore:
outbound:
retry: retryForever
circuitBreaker: simpleCB
In a new terminal window, run the following command to stop Redis:
docker stop dapr_redis
Once Redis is stopped, the requests begin to fail and the retry policy titled retryForever is applied. The output below shows the logs from the order-processor service:
INFO[0006] Error processing operation component[statestore] output. Retrying...
As per the retryFroever policy, retries will continue for each failed request indefinitely, in 5 second intervals.
retryForever:
policy: constant
maxInterval: 5s
maxRetries: -1
Once 5 consecutive retries have failed, the circuit breaker policy, simpleCB, is tripped and the breaker opens, halting all requests:
INFO[0026] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from closed to open
circuitBreakers:
simpleCB:
maxRequests: 1
timeout: 5s
trip: consecutiveFailures >= 5
After 5 seconds has surpassed, the circuit breaker will switch to a half-open state, allowing one request through to verify if the fault has been resolved. If the request continues to fail, the circuit will trip back to the open state.
INFO[0031] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from open to half-open
INFO[0031] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from half-open to open
INFO[0036] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from open to half-open
INFO[0036] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from half-open to closed
This half-open/open behavior will continue for as long as the Redis container is stopped.
Step 3: Remove the fault
Once you restart the Redis container on your machine, the application will recover seamlessly, picking up where it left off.
docker start dapr_redis
INFO[0036] Recovered processing operation component[statestore] output.
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '5' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '5' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '6' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '6' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '7' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '7' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '8' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '8' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '9' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '9' }
Pre-requisites
For this example, you will need:
Step 1: Set up the environment
Clone the sample provided in the Quickstarts repo.
git clone https://github.com/dapr/quickstarts.git
In a terminal window, navigate to the order-processor directory.
cd ../state_management/javascript/sdk/order-processor
Install dependencies
npm install
Step 2: Run the application with resiliency enabled
Run the order-processor service alongside a Dapr sidecar. In the dapr run command below, the --config parameter applies a Dapr configuration that enables the resiliency feature. By enabling resiliency, the resiliency spec located in the components directory is loaded by the order-processor sidecar. The resilency spec is:
apiVersion: dapr.io/v1alpha1
kind: Resiliency
metadata:
name: myresiliency
scopes:
- checkout
spec:
policies:
retries:
retryForever:
policy: constant
maxInterval: 5s
maxRetries: -1
circuitBreakers:
simpleCB:
maxRequests: 1
timeout: 5s
trip: consecutiveFailures >= 5
targets:
apps:
order-processor:
retry: retryForever
circuitBreaker: simpleCB
dapr run --app-id order-processor --config ../config.yaml --components-path ../../../components/ -- npm start
Once the application has started, the order-processorservice writes and reads orderId key/value pairs to the statestore Redis instance defined in the statestore.yaml component.
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '1' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '1' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '2' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '2' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '3' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '3' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '4' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '4' }
Step 3: Introduce a fault
Simulate a fault by stopping the Redis container instance that was initialized when executing dapr init on your development machine. Once the instance is stopped, write and read operations from the order-processor service begin to fail.
Since the resiliency.yaml spec defines statestore as a component target, all failed requests will apply retry and circuit breaker policies:
targets:
components:
statestore:
outbound:
retry: retryForever
circuitBreaker: simpleCB
In a new terminal window, run the following command to stop Redis:
docker stop dapr_redis
Once Redis is stopped, the requests begin to fail and the retry policy titled retryForever is applied. The output below shows the logs from the order-processor service:
INFO[0006] Error processing operation component[statestore] output. Retrying...
As per the retryFroever policy, retries will continue for each failed request indefinitely, in 5 second intervals.
retryForever:
policy: constant
maxInterval: 5s
maxRetries: -1
Once 5 consecutive retries have failed, the circuit breaker policy, simpleCB, is tripped and the breaker opens, halting all requests:
INFO[0026] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from closed to open
circuitBreakers:
simpleCB:
maxRequests: 1
timeout: 5s
trip: consecutiveFailures >= 5
After 5 seconds has surpassed, the circuit breaker will switch to a half-open state, allowing one request through to verify if the fault has been resolved. If the request continues to fail, the circuit will trip back to the open state.
INFO[0031] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from open to half-open
INFO[0031] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from half-open to open
INFO[0036] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from open to half-open
INFO[0036] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from half-open to closed
This half-open/open behavior will continue for as long as the Redis container is stopped.
Step 3: Remove the fault
Once you restart the Redis container on your machine, the application will recover seamlessly, picking up where it left off.
docker start dapr_redis
INFO[0036] Recovered processing operation component[statestore] output.
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '5' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '5' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '6' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '6' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '7' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '7' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '8' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '8' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '9' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '9' }
Pre-requisites
For this example, you will need:
Step 1: Set up the environment
Clone the sample provided in the Quickstarts repo.
git clone https://github.com/dapr/quickstarts.git
In a terminal window, navigate to the order-processor directory.
cd ../state_management/csharp/sdk/order-processor
Install dependencies
dotnet restore
dotnet build
Step 2: Run the application with resiliency enabled
Run the order-processor service alongside a Dapr sidecar. In the dapr run command below, the --config parameter applies a Dapr configuration that enables the resiliency feature. By enabling resiliency, the resiliency spec located in the components directory is loaded by the order-processor sidecar. The resilency spec is:
apiVersion: dapr.io/v1alpha1
kind: Resiliency
metadata:
name: myresiliency
scopes:
- checkout
spec:
policies:
retries:
retryForever:
policy: constant
maxInterval: 5s
maxRetries: -1
circuitBreakers:
simpleCB:
maxRequests: 1
timeout: 5s
trip: consecutiveFailures >= 5
targets:
apps:
order-processor:
retry: retryForever
circuitBreaker: simpleCB
dapr run --app-id order-processor --config ../config.yaml --components-path ../../../components/ -- dotnet run
Once the application has started, the order-processorservice writes and reads orderId key/value pairs to the statestore Redis instance defined in the statestore.yaml component.
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '1' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '1' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '2' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '2' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '3' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '3' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '4' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '4' }
Step 3: Introduce a fault
Simulate a fault by stopping the Redis container instance that was initialized when executing dapr init on your development machine. Once the instance is stopped, write and read operations from the order-processor service begin to fail.
Since the resiliency.yaml spec defines statestore as a component target, all failed requests will apply retry and circuit breaker policies:
targets:
components:
statestore:
outbound:
retry: retryForever
circuitBreaker: simpleCB
In a new terminal window, run the following command to stop Redis:
docker stop dapr_redis
Once Redis is stopped, the requests begin to fail and the retry policy titled retryForever is applied. The output below shows the logs from the order-processor service:
INFO[0006] Error processing operation component[statestore] output. Retrying...
As per the retryFroever policy, retries will continue for each failed request indefinitely, in 5 second intervals.
retryForever:
policy: constant
maxInterval: 5s
maxRetries: -1
Once 5 consecutive retries have failed, the circuit breaker policy, simpleCB, is tripped and the breaker opens, halting all requests:
INFO[0026] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from closed to open
circuitBreakers:
simpleCB:
maxRequests: 1
timeout: 5s
trip: consecutiveFailures >= 5
After 5 seconds has surpassed, the circuit breaker will switch to a half-open state, allowing one request through to verify if the fault has been resolved. If the request continues to fail, the circuit will trip back to the open state.
INFO[0031] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from open to half-open
INFO[0031] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from half-open to open
INFO[0036] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from open to half-open
INFO[0036] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from half-open to closed
This half-open/open behavior will continue for as long as the Redis container is stopped.
Step 3: Remove the fault
Once you restart the Redis container on your machine, the application will recover seamlessly, picking up where it left off.
docker start dapr_redis
INFO[0036] Recovered processing operation component[statestore] output.
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '5' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '5' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '6' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '6' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '7' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '7' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '8' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '8' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '9' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '9' }
Pre-requisites
For this example, you will need:
- Dapr CLI and initialized environment.
- Java JDK 11 (or greater):
- Oracle JDK, or
- OpenJDK
- Apache Maven, version 3.x.
Step 1: Set up the environment
Clone the sample provided in the Quickstarts repo.
git clone https://github.com/dapr/quickstarts.git
In a terminal window, navigate to the order-processor directory.
cd ../state_management/java/sdk/order-processor
Install dependencies
mvn clean install
Step 2: Run the application with resiliency enabled
Run the order-processor service alongside a Dapr sidecar. In the dapr run command below, the --config parameter applies a Dapr configuration that enables the resiliency feature. By enabling resiliency, the resiliency spec located in the components directory is loaded by the order-processor sidecar. The resilency spec is:
apiVersion: dapr.io/v1alpha1
kind: Resiliency
metadata:
name: myresiliency
scopes:
- checkout
spec:
policies:
retries:
retryForever:
policy: constant
maxInterval: 5s
maxRetries: -1
circuitBreakers:
simpleCB:
maxRequests: 1
timeout: 5s
trip: consecutiveFailures >= 5
targets:
apps:
order-processor:
retry: retryForever
circuitBreaker: simpleCB
dapr run --app-id order-processor --config ../config.yaml --components-path ../../../components/ -- java -jar target/OrderProcessingService-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
Once the application has started, the order-processorservice writes and reads orderId key/value pairs to the statestore Redis instance defined in the statestore.yaml component.
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '1' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '1' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '2' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '2' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '3' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '3' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '4' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '4' }
Step 3: Introduce a fault
Simulate a fault by stopping the Redis container instance that was initialized when executing dapr init on your development machine. Once the instance is stopped, write and read operations from the order-processor service begin to fail.
Since the resiliency.yaml spec defines statestore as a component target, all failed requests will apply retry and circuit breaker policies:
targets:
components:
statestore:
outbound:
retry: retryForever
circuitBreaker: simpleCB
In a new terminal window, run the following command to stop Redis:
docker stop dapr_redis
Once Redis is stopped, the requests begin to fail and the retry policy titled retryForever is applied. The output below shows the logs from the order-processor service:
INFO[0006] Error processing operation component[statestore] output. Retrying...
As per the retryFroever policy, retries will continue for each failed request indefinitely, in 5 second intervals.
retryForever:
policy: constant
maxInterval: 5s
maxRetries: -1
Once 5 consecutive retries have failed, the circuit breaker policy, simpleCB, is tripped and the breaker opens, halting all requests:
INFO[0026] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from closed to open
circuitBreakers:
simpleCB:
maxRequests: 1
timeout: 5s
trip: consecutiveFailures >= 5
After 5 seconds has surpassed, the circuit breaker will switch to a half-open state, allowing one request through to verify if the fault has been resolved. If the request continues to fail, the circuit will trip back to the open state.
INFO[0031] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from open to half-open
INFO[0031] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from half-open to open
INFO[0036] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from open to half-open
INFO[0036] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from half-open to closed
This half-open/open behavior will continue for as long as the Redis container is stopped.
Step 3: Remove the fault
Once you restart the Redis container on your machine, the application will recover seamlessly, picking up where it left off.
docker start dapr_redis
INFO[0036] Recovered processing operation component[statestore] output.
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '5' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '5' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '6' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '6' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '7' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '7' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '8' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '8' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '9' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '9' }
Pre-requisites
For this example, you will need:
Step 1: Set up the environment
Clone the sample provided in the Quickstarts repo.
git clone https://github.com/dapr/quickstarts.git
In a terminal window, navigate to the order-processor directory.
cd ../state_management/go/sdk/order-processor
Install dependencies
go build .
Step 2: Run the application with resiliency enabled
Run the order-processor service alongside a Dapr sidecar. In the dapr run command below, the --config parameter applies a Dapr configuration that enables the resiliency feature. By enabling resiliency, the resiliency spec located in the components directory is loaded by the order-processor sidecar. The resilency spec is:
apiVersion: dapr.io/v1alpha1
kind: Resiliency
metadata:
name: myresiliency
scopes:
- checkout
spec:
policies:
retries:
retryForever:
policy: constant
maxInterval: 5s
maxRetries: -1
circuitBreakers:
simpleCB:
maxRequests: 1
timeout: 5s
trip: consecutiveFailures >= 5
targets:
apps:
order-processor:
retry: retryForever
circuitBreaker: simpleCB
dapr run --app-id order-processor --config ../config.yaml --components-path ../../../components -- go run .
Once the application has started, the order-processorservice writes and reads orderId key/value pairs to the statestore Redis instance defined in the statestore.yaml component.
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '1' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '1' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '2' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '2' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '3' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '3' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '4' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '4' }
Step 3: Introduce a fault
Simulate a fault by stopping the Redis container instance that was initialized when executing dapr init on your development machine. Once the instance is stopped, write and read operations from the order-processor service begin to fail.
Since the resiliency.yaml spec defines statestore as a component target, all failed requests will apply retry and circuit breaker policies:
targets:
components:
statestore:
outbound:
retry: retryForever
circuitBreaker: simpleCB
In a new terminal window, run the following command to stop Redis:
docker stop dapr_redis
Once Redis is stopped, the requests begin to fail and the retry policy titled retryForever is applied. The output belows shows the logs from the order-processor service:
INFO[0006] Error processing operation component[statestore] output. Retrying...
As per the retryFroever policy, retries will continue for each failed request indefinitely, in 5 second intervals.
retryForever:
policy: constant
maxInterval: 5s
maxRetries: -1
Once 5 consecutive retries have failed, the circuit breaker policy, simpleCB, is tripped and the breaker opens, halting all requests:
INFO[0026] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from closed to open
circuitBreakers:
simpleCB:
maxRequests: 1
timeout: 5s
trip: consecutiveFailures >= 5
After 5 seconds has surpassed, the circuit breaker will switch to a half-open state, allowing one request through to verify if the fault has been resolved. If the request continues to fail, the circuit will trip back to the open state.
INFO[0031] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from open to half-open
INFO[0031] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from half-open to open
INFO[0036] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from open to half-open
INFO[0036] Circuit breaker "simpleCB-statestore" changed state from half-open to closed
This half-open/open behavior will continue for as long as the Redis container is stopped.
Step 3: Remove the fault
Once you restart the Redis container on your machine, the application will recover seamlessly, picking up where it left off.
docker start dapr_redis
INFO[0036] Recovered processing operation component[statestore] output.
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '5' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '5' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '6' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '6' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '7' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '7' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '8' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '8' }
== APP == Saving Order: { orderId: '9' }
== APP == Getting Order: { orderId: '9' }
Tell us what you think!
We’re continuously working to improve our Quickstart examples and value your feedback. Did you find this quickstart helpful? Do you have suggestions for improvement?
Join the discussion in our discord channel.
Next steps
Learn more about the resiliency feature and how it works with Dapr’s building block APIs.
Explore Dapr tutorials >>Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.